Project 3. Epigenetics in embryonic stem cell neurogenesis
J. Cell. Physiol. 219 (2): 243-50 (2009)
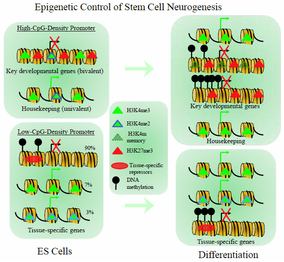
Epigenetic mechanisms control gene expression and dictate changes in the cellular phenotypes without direct involvement of the underlying DNA sequences. Embryonic stem cells are derived from the inner cell mass of the blastocyst and have the properties of self-renewal and differentiation into all derivatives of the three primary germ layers. In our lab, we differentiate embryonic stem cells towards specific cell types and study the role of epigenetics during the process of differentiation. Among the induced genes during embryonic stem (ES) cell neurogenesis, we have a clear focus on MeCP2 isoforms with direct link to compromised brain function, Rett Syndrome, and Autism Spectrum Disorders (ASD). Our genomic and epigenetic approaches will result in a better understanding of gene expression during stem cell differentiation with future applications in stem cell-based therapy strategies of human neurological disorders.